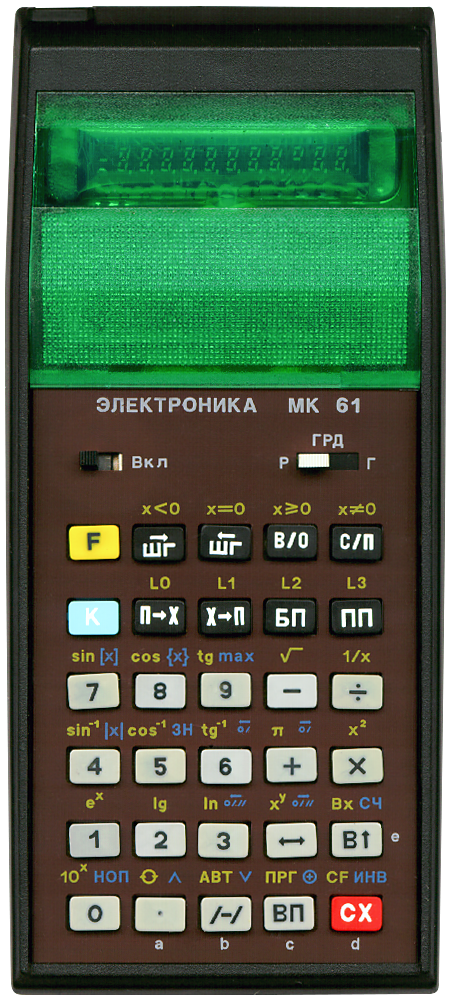
Terminated: 1994
It has 105 steps of programming memory and 15 memory registers. It has all the common scientific functions and can also pertform logical operations, in a way. Calculations are performed using RPN and it has a 4-level RPN stack.
It looks as being inspired by the HP 41C but it feels less sturdy, especially its keyboard. Still, its shape is beautiful.
The ELEKTRONIKA MK 61 is the non-extendable sibling of the ELEKTRONIKA MK 52.
On my scan (and on some other scans I find online) the faceplate looks brown. It is actually not brown but black. For some reason my scanner detects it as being brown.
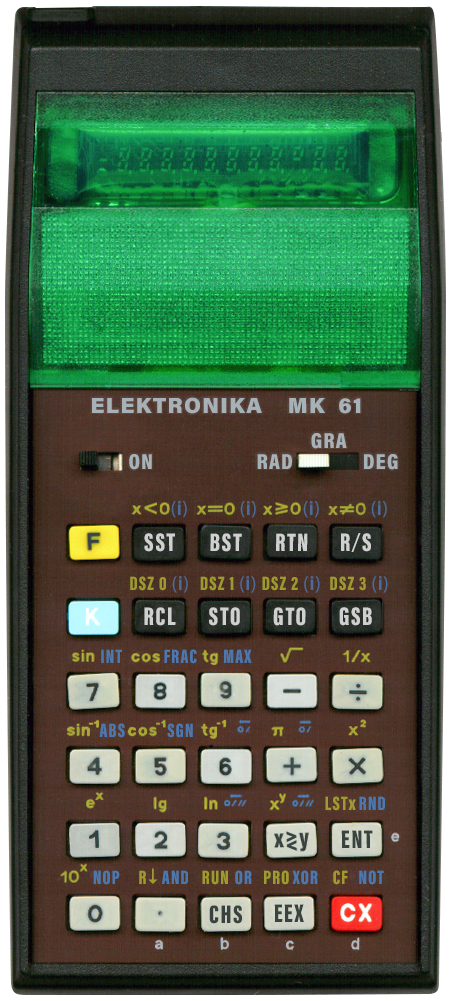
 Its Cyrillic keyboard might be intimidating at first. The manual,
in Russian, does not help either if one does not understand Russian.
Fortunately Jose Mesquita created an English translation of its manual. This manual
can be downloaded as a pdf file on wass.net
here (link validated 2025-12-28).
Also very helpful is the MK 61 command reference
found
here (link validated 2025-12-28)
on Thimet.
Its Cyrillic keyboard might be intimidating at first. The manual,
in Russian, does not help either if one does not understand Russian.
Fortunately Jose Mesquita created an English translation of its manual. This manual
can be downloaded as a pdf file on wass.net
here (link validated 2025-12-28).
Also very helpful is the MK 61 command reference
found
here (link validated 2025-12-28)
on Thimet.
Using these references and the translated manual I have created my own English and usable rendering of how an English version of this calculator could have looked. Click on the small image of the calculator shown here to see it. To reduce clutter I use a blue "(i)" to indicate the functions that can use indirect addressing when used with the K modifier key. Furthermore I try to use HP like symbols and lettering. I tried to be as close to the original colouring as possible.
Some noteworthy knowledge:
- The СF function (Сброс F; F СX) is not to clear flags, it is to cancel the accidental usage of the F modifier key. This calculator does not have user settable flags.
- The СЧ function (псевдоСлучайного Числа; K В↑) generates pseudo-random numbers between 0 and 1.
- Use the НОП function (Нет ОПерации; K 0) to insert a NOP whilst editing a program. A NOP does not do anything but take up space and is recognisable, it shows up as "54". It can also be selected, in RUN mode, to clear having accidentally pressed the K modifier key.
- When in АВТ (АВТоматическая работа; RUN) mode, the ПП key can be used to single step through a program.
- Fractional numbers smaller than 1 can not be entered by keying . followed by the fractional part as common on most other calculators. Start by keying 0 . first, followed by the fractional part.
- There is the following safety measure mentioned in the (translated) manual: "After turning off the MK, allow a minimum of 30 seconds before switching it on again". I must confess that I not always do that, I am yet to find out what can go wrong.
- ∧ for AND.
- ∨ for OR.
- ⊕ for XOR.
- ИНВ (INV) for INVERSE.
Alfred Klomp has a nice writeup on this part of this calculator, read it here (link validated 2025-12-30).
Since this is a programmable calculator, here is a simple programming example, multiply anything by 42:
Start programming mode:
Now, type any number followed by С/П to multiply
it by 42.
ПРГ
(PRG, from Программирование; by keying F ВП)
Enter the program:
В↑
4
2
×
С/П (stop program)
В/0 (jump to start after resuming program)
End programming mode, return to RUN mode:
АВТ
(Автоматическая работа; by keying F /−/)
And jump to the start of the program:
В/0
More elaborate programming is of course possible. It has multiple memories and has indirect addressing for memory, jumps and subroutines. Programs can also be edited.
Here is another programming example: calculate the factorial of a number. It has a loop with a confitional jump using register '0' as a counter:
Start programming mode:
Now calculate the factorial of 69 by keying
6 9 С/П and
have some patience. This
calculator is not very quick, it takes 1 minute and 20 seconds to calculate the result.
ПРГ (F ВП)
Enter the program:
X→П 0 (store in register 0)
1
П→X 0 (recall register 0)
×
L0 (F П→X)
0
2 (decrease register 0, jump to 02, the third line here, when non-zero)
С/П (stop program)
End programming mode, return to RUN mode:
АВТ (F /−/)
And jump to the start of the program:
В/0
Beware that this calculator does not have constant memory, any programming and memory data is lost when the calculator is switched off.
What I find particularly nice is the fact that it comes with the calculator’s schematics in the box.
By the way, I bought this calculator on eBay from Ukraine in 2025.