
Terminated: unknown
It has the common scientific functions such as trigonometric functions, logarithms and their exponential counterparts, a key for sexagesimal conversion and it has memory.
The exponent is 2-digit but is limited to the range of -39 to 39. The lowest and highest values possible are therefore -9.99999 × 10-39 and 9.99999 × 1039, the smallest being 1 × 1039 (smaller numbers are rounded off to zero).
The display has a peculiarity, the zero is lower case! I don’t know any other calculator series apart from the early CASIO’s that have a lower case zero.
The number 170.50 for example looks like this:
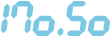
When the calculator is calculating a result then rightmost digit’s segments flicker randomly to indicate the work in progress.
The workings of the xy key might be puzzling to users of this calculator. When you enter a (positive) number and press the xy key an intermediate result is shown, being the natural log "ln" of the number entered. To obtain its power enter the value for y and press the = key. My guess is that this calculator uses this formula:
xy = e(y · ln x)
This works nicely for positive values of x but will result in an
error when x is zero or less. Not a big problem because powers of negavive
numbers behave counter intuitive anyway (producing non-complex results
only for integer values of y or fractional values of y with an odd
denominator).
This calculator has separate keys for the exponent and the constant π instead of the combined key of most other scientific calculators by CASIO (where the EXP key will enable you to enter the exponent when you first enter digits, and will otherwise enter the constant π).
There’s no INV key, but there is an arc key for the inverse trigonometric functions.